A consensus document on anaesthesia and sedation in breastfeeding women has been produced by members of a Working Party established by the Association of Anaesthetists of Great Britain and Ireland and has been informed by the UNICEF UK Baby Friendly Initiative and endorsed by the RCM and RCOG.
The document reviews the pharmacokinetics of drugs commonly used during anaesthesia so that professionals can undertake a risk‐benefit discussion with the woman, and provides guidance on the development of local policies for staff. Based on the evidence, breastfeeding is acceptable to continue after anaesthesia and should be supported as soon as the woman is alert and able to breastfeed. It is emphasised that breastmilk should not be discarded, which can commonly occur alongside interruption and/or cessation of breastfeeding as a result of inconsistent information from health professionals to mothers who require anaesthesia or sedation.
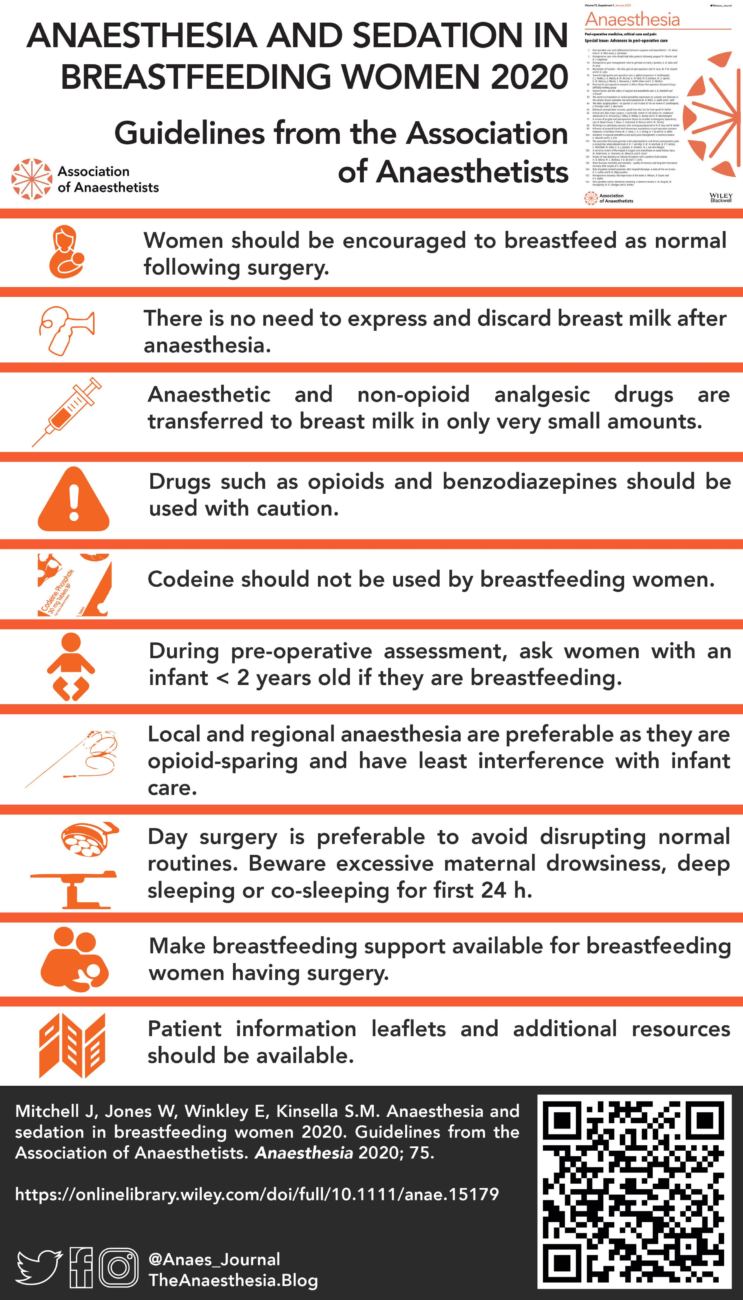
Ten key recommendations on anaesthesia and sedation in breastfeeding women are provided, including that breastfeeding support should be accessible for lactating women undergoing surgical and medical procedures and that patient information leaflets and additional resources should be available containing information on the compatibility of anaesthetic agents and analgesics during breastfeeding.
For more information on breastfeeding, see our range of helpful resources. You can read the consensus document in its entirety here.
The infographic below by the Association of Anaesthetists provides additional detail on the guidance:
(c) Association of Anaesthetists





